Autor: Robert Luo
En este artículo
If you’ve ever wondered about the elusive panther, you’re not alone. Many people seek panther animal information to understand these fascinating creatures better, often asking questions like, “What do panthers eat?” or “Are they endangered?” Finding a comfortable solution for your curiosity can be challenging amidst the overwhelming amount of data available. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive overview of panthers, exploring their habitat, behavior, diet, and conservation status. Whether you’re a student, a wildlife enthusiast, or just curious, our detailed insights will equip you with all the necessary knowledge about these majestic animals. Let’s dive into the world of panthers!
* **Problem Solving:** Users are asking specific questions like ‘- What are the different species of panthers?’ and ‘- Where do panthers typically live?’. This shows they have specific problems they need to solve regarding ‘panther animal information’.
Este artículo pretende satisfacer todas estas necesidades proporcionando explicaciones exhaustivas, guías prácticas e información comparativa.
Panthers are large, powerful cats that belong to the genus Puma, with the most well-known species being the Florida panther and the black panther, which is a melanistic variant of leopards or jaguars.
They are solitary animals, primarily active at dusk and dawn (crepuscular), and have excellent night vision, making them effective hunters.
Panthers inhabit a variety of ecosystems, including forests, swamps, and grasslands, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their habitats as apex predators.
Their populations are threatened due to habitat loss, hunting, and genetic diversity issues, making conservation efforts vital for their survival.
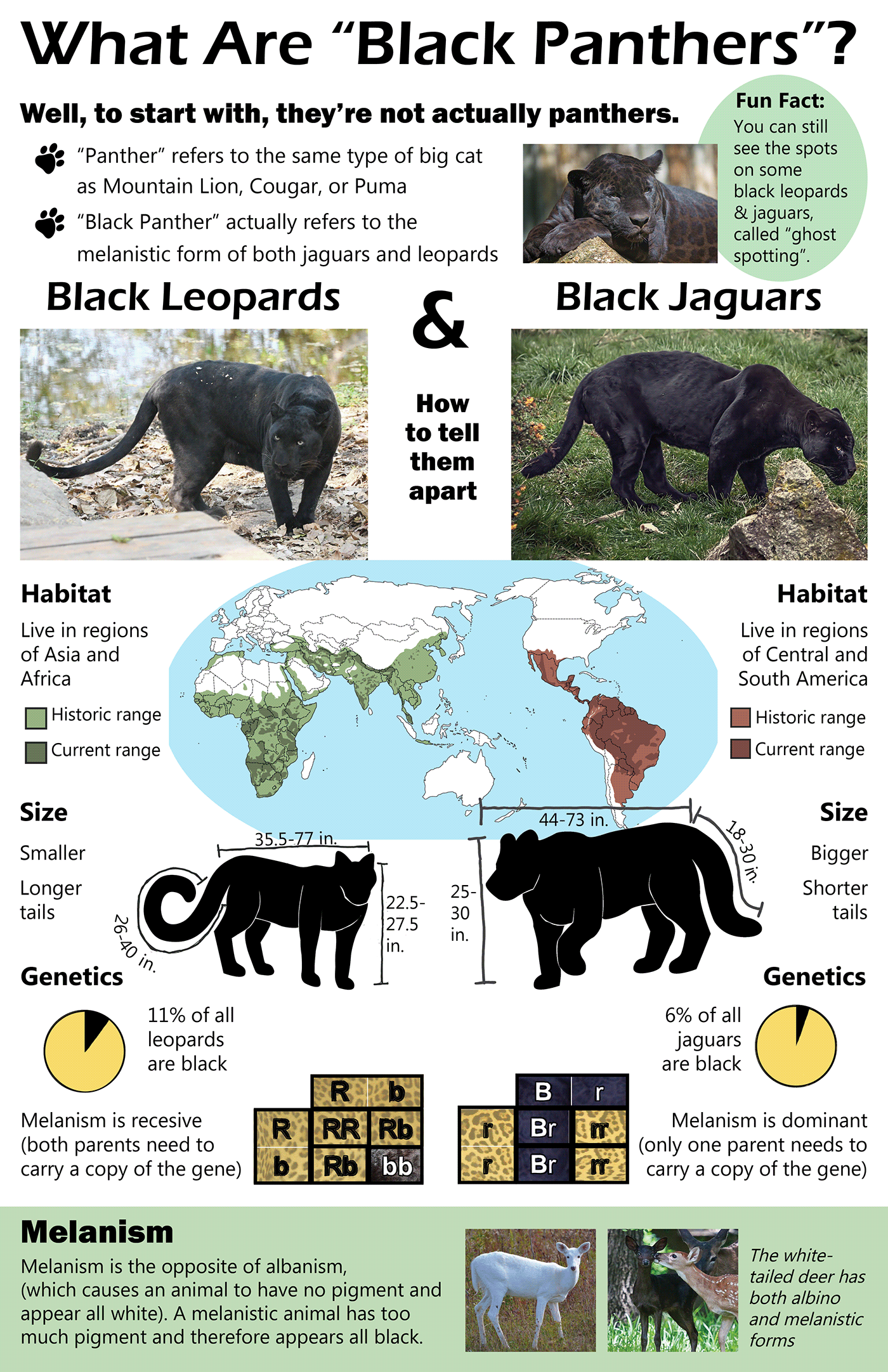
The term “panther” is commonly used to refer to large cats belonging to the genus Panthera, particularly the leopard (Panthera pardus) and the jaguar (Panthera onca). In a more specific context, the term may also refer to the melanistic color variant of these species, which are characterized by their dark fur. Panthers are renowned for their stealth, strength, and adaptability, making them fascinating subjects for both wildlife enthusiasts and researchers alike.
The panther, as a term, encompasses various species and characteristics that make these animals unique and captivating. Below, we will explore various aspects of panthers, including their classification, habitat, diet, speed, and more.
The term “panther” can refer to several species within the Panthera genus. The most commonly recognized are:
Known for their powerful build and distinctive rosette-patterned coat.
Leopard (Panthera pardus):
Also has a rosette-patterned coat but is generally smaller than the jaguar.
Melanistic Variants:
Often referred to as “black panthers,” these are not a separate species but rather color variants of leopards and jaguars. Their dark fur can make their rosettes less visible.
Clouded Leopard (Neofelis nebulosa):
Found in Southeast Asia and characterized by its large cloud-like spots.
Sunda Clouded Leopard (Neofelis diardi):
Panthers inhabit a variety of environments, from dense tropical rainforests to arid grasslands. Their adaptability allows them to thrive in diverse ecosystems. Here are some specific habitats:
Jaguars: Primarily found in tropical rainforests, jaguars also inhabit swamps, mangroves, and scrublands. They are often associated with water sources, as they are excellent swimmers.
Leopards: These cats are incredibly versatile and can be found in savannas, grasslands, dense forests, and even mountainous areas. Their adaptability to different environments is one of their greatest strengths.
Clouded Leopards: Prefer dense, tropical forests with plenty of trees for climbing and hunting. They are usually found in the Himalayan foothills down to Southeast Asia.
Melanistic Panthers: The habitats of melanistic panthers are the same as their non-melanistic counterparts, as this coloration occurs in both jaguars and leopards.
Panthers are carnivorous predators, and their diet varies depending on their species and habitat. Here are some details about their feeding habits:
Jaguar: Jaguars have a diverse diet that includes deer, capybaras, and even caimans. Their powerful jaw allows them to pierce through turtle shells to access the meat inside.
Leopard: Leopards are opportunistic feeders and will eat a wide range of animals, including antelope, rodents, and birds. They are known for their ability to haul prey up into trees to avoid competition from other predators.
Clouded Leopard: Their diet consists mainly of birds, small mammals, and monkeys. They are agile climbers, which allows them to hunt effectively in trees.
Melanistic Panthers: The feeding habits of melanistic panthers mirror those of their respective species, whether jaguars or leopards.
The speed of panthers varies by species. Here are some general estimates:
Jaguar: Jaguars can reach speeds of up to 50 km/h (31 mph) in short bursts, making them powerful hunters.
Leopard: Leopards can run at speeds of up to 58 km/h (36 mph), which assists them in catching prey and escaping threats.
Clouded Leopard: Although not as fast as their larger relatives, clouded leopards are agile climbers and can reach speeds of about 40 km/h (25 mph) on the ground.
Overall, these big cats rely on stealth and strength rather than speed for hunting, often stalking their prey and launching surprise attacks.
Understanding panthers involves exploring several core factors and components, including their biology, behavior, and conservation status.
Size and Weight: Jaguars are the largest of the panther species, weighing between 45 to 113 kg (100 to 250 lbs). Leopards generally weigh around 20 to 90 kg (44 to 198 lbs).
Coloration: While leopards and jaguars can be melanistic, they typically feature distinctive rosettes that help with camouflage in their respective environments.
Solitary Nature: Panthers are predominantly solitary animals, except for mothers with cubs. They establish territories that they actively defend from other panthers.
Hunting Techniques: Panthers employ different hunting strategies depending on their species. Jaguars often use a “stalk and ambush” technique, while leopards might use a combination of stealth and speed.
Reproductive Habits: Female panthers typically give birth to 1-4 cubs after a gestation period of about 90-110 days. Cubs are born blind and rely on their mother for nourishment and protection.
Lifespan: In the wild, panthers may live up to 10-15 years, while those in captivity can live longer due to a lack of natural predators and consistent food supply.
Threats: Panthers face numerous threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Jaguars, in particular, are classified as Near Threatened by the IUCN, while leopards are listed as Vulnerable.
Conservation Efforts: Various organizations and governments are working to protect panther habitats and mitigate human-wildlife conflict through education and community engagement.
When discussing panther information, it’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of understanding these magnificent creatures.
Ecosystem Indicators: Panthers serve as apex predators, playing a crucial role in maintaining the balance of their ecosystems by controlling prey populations.
Biodiversity Awareness: Knowledge of panthers fosters a greater appreciation for biodiversity and the importance of wildlife conservation.
Research Opportunities: Studying panthers provides insights into behavior, genetics, and evolution, which can inform broader ecological studies.
Misconceptions: The term “panther” can lead to confusion among the public due to its varied usage, potentially misinforming conservation messages.
Human-Wildlife Conflict: Increased knowledge about panthers can sometimes heighten fears and lead to conflict, particularly in areas where panthers and humans coexist.
Conservation Challenges: Efforts to protect panthers can be met with resistance from local communities, especially if they perceive these animals as threats to livestock or livelihoods.
Understanding panther information has several practical applications, ranging from conservation efforts to educational programs.
Organizations like Panthera and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) actively work on initiatives aimed at protecting panther habitats and raising awareness about their plight.
In regions where panthers are prevalent, ecotourism can be a sustainable way to generate income while promoting conservation. Safaris and wildlife tours focused on spotting panthers can support local economies and incentivize habitat preservation.

Schools and community programs focused on wildlife education can help dispel myths about panthers, fostering a more positive relationship between humans and these majestic animals.
Researchers utilize various technologies, such as GPS collars, to monitor panther populations and movements. This data aids in understanding their behavior and helps inform conservation strategies.
In summary, panthers are a captivating group of large cats that embody strength, agility, and adaptability. Whether referring to jaguars, leopards, or their melanistic variants, these animals play vital roles in their ecosystems and are integral to biodiversity. While they face significant threats, concerted conservation efforts and increased public awareness can help ensure their survival for future generations. Understanding panther animal information not only enriches our knowledge of these magnificent creatures but also underscores the importance of protecting their habitats and fostering coexistence with human communities.
Panthers communicate through vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. They use growls, roars, and hisses to convey messages to other panthers.
While not all panther species are endangered, the jaguar and leopard populations are under threat due to habitat loss and poaching. Conservation status varies by region and species.
Yes, both jaguars and leopards are excellent swimmers. Jaguars, in particular, are known for their affinity for water and often hunt aquatic prey.
Panthers typically employ a combination of stealth and strength to hunt. They stalk their prey and use powerful ambush tactics to catch them off guard.
Panthers possess several adaptations, including keen eyesight, strong limbs for climbing and jumping, and acute hearing that aids in detecting prey.

This comprehensive guide to panther animal information aims to provide a thorough understanding of these remarkable creatures, their habitats, diets, behaviors, and the challenges they face.
When searching for information about panthers, users often encounter various challenges that can be frustrating. Here are three common pain points, complete with relatable scenarios and practical solutions to help you navigate this topic effectively.
Escenario de usuario:
Jessica, a high school biology teacher, is preparing a lesson on big cats. She wants to include information about panthers but realizes that the term “panther” can refer to multiple species, including leopards and cougars. Confused about which specific animal she should focus on, she struggles to find clear and accurate information that distinguishes these species.
Solución:
To address this issue, educators and enthusiasts should clarify that “panther” commonly refers to two main species: the black leopard (Panthera pardus) and the Florida panther (Puma concolor coryi). Here’s how to approach this:
Escenario de usuario:
Mark is an animal enthusiast who loves visiting zoos and wildlife parks. He notices that people often misunderstand panther behavior, believing they are aggressive and dangerous. Mark wants to educate his friends about the true nature of panthers but finds it challenging to convey the nuances of their behavior without sounding overly technical.
Solución:
To help clarify panther behavior and dispel myths, follow these steps:
Escenario de usuario:
Emily, a college student studying environmental science, is passionate about wildlife conservation. She learns about the endangered status of the Florida panther but is disheartened by misconceptions surrounding their conservation efforts. Many of her classmates believe that panthers are beyond saving, which frustrates her.
Solución:
To combat these myths and promote awareness, Emily can take the following actions:
By addressing these common pain points and providing clear solutions, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of panthers and contribute positively to their conservation efforts.
The keyword “panther animal information” likely refers to a general search for details about panthers, which are often associated with big cats like leopards and cougars. Since it does not appear to be a product or brand, we can consider it as a method of gathering information about panthers. Below, I’ve identified two alternative methods for acquiring animal information and created a comparison table to highlight their features and benefits.
| Característica | Panther Animal Information | Alternative 1: Wildlife Documentaries | Alternative 2: Online Databases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Format | Textual Information | Video Format | Textual & Multimedia |
| Accessibility | Readily available online | Available on streaming platforms | Accessible via web browsers |
| Depth of Information | Moderate | Alta | Alta |
| Engagement | Bajo | High (visual and auditory) | Moderate (varies by database) |
| Updates | Static | Regularly updated | Frequently updated |
- Análisis de expertos del sector

Hola, soy el webmaster de lecintech.com, Robert Luo, puedes llamarme Robert. Tengo años de experiencia en el negocio de control de plagas. Nos especializamos en el diseño y fabricación de ahuyentadores ultrasónicos de plagas, ahuyentadores ultrasónicos de mosquitos, ahuyentadores ultrasónicos de roedores, ahuyentadores de animales alimentados por energía solar, trampas de plagas, ahuyentadores de plagas portátiles y mucho más.