Autor: Robert Luo
The Complete Guide to Bed Bug Control: From Identification to Eradication, Say Goodbye to Bed Bug Troubles. In daily life, there exists a tiny pest capable of causing immense distress—the bed bug. Whether in family homes, hotel rooms, or rental apartments, any space can become a bed bug “habitat.” Active primarily at night, they feed on human blood, causing skin irritation, disrupted sleep, and potentially transmitting diseases—posing serious threats to both daily life and health. This comprehensive guide covers bed bug identification, harm symptoms, control methods, prevention strategies, and common misconceptions, equipping you with the knowledge to eliminate bed bug problems once and for all.
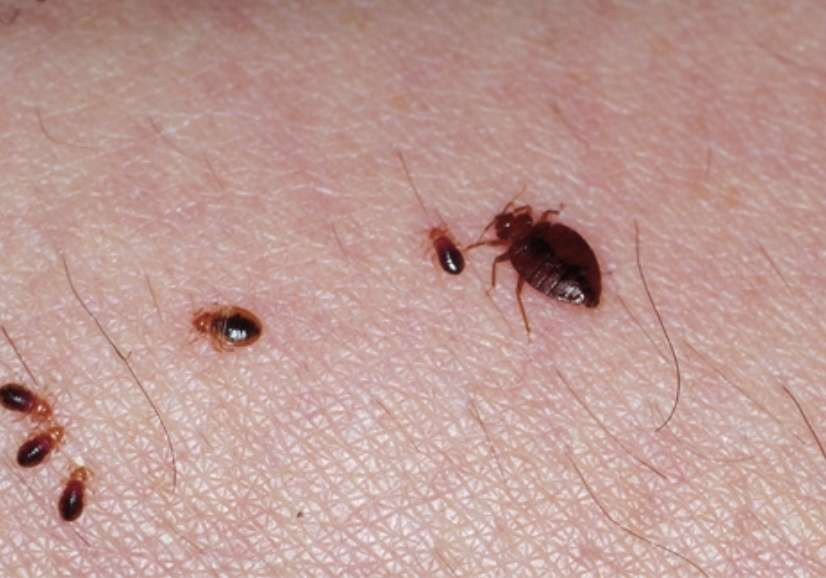
To effectively combat bed bugs, one must first learn to accurately identify them. Bed bugs belong to the family Cimicidae within the order Hemiptera, with common species including the common bed bug and the tropical bed bug. In appearance, bed bugs are small, with adults measuring approximately 4-5 mm in length and 3 mm in width. They have a flattened oval shape, typically brown or dark red in color, and are covered in fine, short hairs, resembling tiny “lentils.” Nymphs are smaller and lighter in color, appearing pale yellow or white. Their color gradually darkens as they grow and develop.
In terms of behavior, bed bugs exhibit distinct nocturnal tendencies. During the day, they typically hide in dark, damp places like bed frame cracks, mattress folds, nightstand drawers, wardrobe corners, and wall crevices. Their flattened bodies allow them to squeeze through gaps as narrow as 0.1 millimeters. At night, when humans enter deep sleep, bed bugs use their keen sense of smell and temperature perception to crawl onto human skin to feed on blood. Each feeding session lasts about 5-10 minutes. After feeding, their bodies swell several times in size and their color becomes more vivid.
Bed bugs exhibit extraordinary reproductive capacity. A single female can lay 200-500 eggs in her lifetime. These eggs measure about 0.5 millimeters, are white and oval-shaped, and are often attached to crevices. Under optimal temperature (25-30°C) and humidity conditions, eggs hatch into nymphs within 1-2 weeks. After five molts, nymphs develop into adults, completing their entire life cycle in just 30-50 days. This rapid growth cycle explains why bed bugs can proliferate massively within a short timeframe if infestations are not addressed promptly.
Many people believe bed bugs merely cause “itchy bites” and are no big deal. However, the harm they inflict extends far beyond this. Their impact on human health, quality of life, and living environments cannot be overlooked.
1. Threats to Human Health: Triggering Skin Issues and Disease Risks
When bed bugs bite, they secrete saliva containing anesthetic components to prevent detection. This saliva also triggers allergic reactions in humans. After a bite, the skin develops red papules or blisters accompanied by intense itching, particularly worsening at night and severely disrupting sleep quality. Scratching the affected areas can easily break the skin, leading to bacterial infections that may develop into pustules, folliculitis, or other skin conditions. It may even trigger allergic reactions like eczema or hives.
Additionally, while no conclusive evidence exists that bed bugs transmit serious infectious diseases like HIV or hepatitis B, research indicates they may carry pathogens such as Yersinia pestis (plague bacillus) and Mycobacterium leprae (leprosy bacillus), posing potential disease transmission risks. Prolonged exposure to bed bug bites may also cause psychological issues like anxiety and depression, affecting overall physical and mental health.
2. Impact on Quality of Life: Disruption of Living Environments and Daily Routines
Bed bugs not only bite humans but also leave behind copious amounts of feces and molted skins in their habitats. These substances emit a foul odor, which becomes more pronounced with larger infestations, severely contaminating living spaces. Additionally, bed bugs can attach themselves to clothing, bedding, luggage, and other items, spreading to new locations through human travel and causing distress to households and others.
For the hospitality industry, including hotels and bed-and-breakfasts, bed bug infestations are particularly devastating. If guests discover bed bugs in a hotel room, it not only leads to complaints and refund requests but also spreads negative publicity through social media and review platforms. This severely damages the hotel’s reputation and customer traffic, resulting in significant financial losses.
3. Increased Economic Costs: Time and Money Consumed by Control Processes
Addressing bed bug infestations demands substantial time and financial investment. Households must purchase pesticides, bed bug-proof mattress covers, vacuum cleaners, and other control supplies, while also dedicating time to cleaning rooms and laundering bedding. Severe infestations beyond DIY control require hiring professional pest control services, which typically incur high costs—a single treatment can reach thousands of dollars. Furthermore, during the treatment process, heavily infested furniture, mattresses, and other items may need to be discarded, adding to the financial burden.
Upon discovering bed bugs in your home or living environment, promptly implement effective control measures to prevent further infestation. Below are several common bed bug control methods; select the most suitable approach based on your specific situation.
1. Physical Control: Safe and Eco-Friendly for Mild Infestations
Physical control directly eliminates bed bugs or disrupts their habitat through non-chemical means. This approach is safe, environmentally friendly, and leaves no chemical residues, making it ideal for mild infestations with few bugs.
① Heat Treatment: Bed bugs are highly sensitive to high temperatures. Exposing them to 60°C (140°F) or higher for 30 minutes kills adults, nymphs, and eggs. Infested clothing, bedding, and sheets can be washed in a washing machine using water above 60°C, followed by high-temperature drying in a dryer. For large furniture like mattresses and sofas, use a steam cleaner to treat surfaces and crevices with high-temperature steam, eliminating hidden bed bugs.
② Low-Temperature Treatment: For items unsuitable for high heat (e.g., woolen garments, leather goods), use low-temperature treatment. Place items in a sealed bag within the freezer compartment, set to -18°C or below, for 24-48 hours to effectively eliminate bed bugs.
③ Physical Removal Method: Thoroughly vacuum areas where bed bugs may hide, including bed frames, mattresses, nightstands, wardrobes, and wall crevices. Pay special attention to dust, excrement, and eggs trapped in crevices. After cleaning, seal the vacuum bag tightly and dispose of it in an outdoor trash bin to prevent reinfestation. Simultaneously, use a stiff-bristled brush to scrub the mattress surface and crevices, dislodging hidden bed bugs and eggs before vacuuming them up.
④ Isolation Protection Method: Cover mattresses and pillows with specialized bed bug-proof covers. These covers feature fine mesh that prevents bed bugs from entering the mattress interior while trapping existing bugs inside, starving them of blood sources until they die. Additionally, wrap bed legs with bed bug-proof leg covers or apply petroleum jelly/talcum powder to the bottom of legs to prevent bed bugs from climbing onto the bed.
2. Chemical Control: Highly Effective and Fast-Acting, but Safety Precautions Required
Chemical control involves using insecticides to eliminate bed bugs. This method is highly effective and fast-acting, suitable for moderate infestations with a significant number of bed bugs. However, safety precautions must be taken when using chemical agents to avoid harm to humans and pets.
① Select appropriate insecticides: Common bed bug pesticides include pyrethroid and organophosphate formulations. Choose products from reputable manufacturers with national pesticide registration certificates, such as permethrin or deltamethrin. Carefully read the instructions before use to understand application methods, suitable areas, and precautions.
② Proper Use of Insecticides: When applying insecticides, first seal all food, tableware, clothing, and other items in the room to prevent chemical contamination. Focus spraying on bed bug hiding spots such as bed frame crevices, mattress folds, nightstand drawers, wardrobe corners, and wall cracks. Apply evenly to ensure coverage of all potential hiding places. After spraying, close all windows and doors to allow the pesticide to fully take effect for 2-4 hours. Then open windows and doors to ventilate the room. Wait until the odor has completely dissipated before re-entering.
③ Safety Precautions: When using insecticide, wear protective gear such as gloves and a mask to prevent skin contact and inhalation. If elderly individuals, children, pregnant women, or pets are present, relocate them to a safe area and allow them to return only after the chemical has fully dissipated. Do not use insecticide in areas where food is handled, such as kitchens or dining rooms, and never spray it directly onto human skin.
3. Professional Pest Control: Thorough Eradication for Severe InfestationsIf bed bug issues persist after attempting physical and chemical control methods, or if infestations are severe (e.g., bugs found throughout an entire room or multiple rooms), promptly hire a professional pest control company. These companies possess specialized equipment and expertise to conduct comprehensive inspections, develop targeted treatment plans, and completely eliminate bed bugs.Professional treatment typically involves these steps: First, technicians conduct an on-site inspection to determine the infestation’s scope and density. Based on findings, they apply specialized pesticides (such as slow-release agents or powders) to bedbug habitats. They may also use thermal foggers or fumigation to thoroughly treat hard-to-reach crevices and corners. Finally, the pest control company provides follow-up monitoring and prevention recommendations to ensure bed bugs do not reappear. It is important to note that when selecting a professional pest control company, choose one with proper credentials and a good reputation. Avoid unlicensed “black market” intermediaries to prevent property damage or safety hazards.
Preventing bed bugs proactively is far more important than dealing with them after an infestation. By following these daily practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of bed bug intrusion.
1. Upon Returning Home: Conduct Thorough Checks to Prevent Bed Bug Infestation
Traveling or business trips are high-risk scenarios for bed bug transmission, especially in accommodations like hotels and guesthouses where exposure is common. Therefore, after returning home, perform the following inspections:
① Inspect Luggage: Place suitcases in a well-ventilated area like outside the door or on the balcony. Avoid placing them directly on the bed or floor in the bedroom. Open the suitcase and meticulously inspect clothing, lining, zipper crevices, and other areas for adult bed bugs, nymphs, or eggs (tiny white specks).
② Wash Clothing: Place all worn clothing into the washing machine. Wash using hot water above 60°C (140°F) and tumble dry on high heat. Even seemingly clean items require this treatment, as bed bugs may cling to fabric surfaces.
③ Inspect personal items: Thoroughly examine backpacks, handbags, shoes, and other belongings—pay special attention to backpack compartments and shoe interiors. Use a vacuum cleaner to remove dust from crevices or wipe surfaces with a damp cloth.
2. Home Environment: Maintain Cleanliness to Destroy Bed Bug Habitats
Keeping your home clean and dry is key to preventing bed bugs. Focus on these areas:
① Regular cleaning: Perform a thorough household cleaning at least once a week. Vacuum floors, sofas, mattresses, and other surfaces in bedrooms, living rooms, and study areas. Pay special attention to dust-prone spots like under beds, beneath wardrobes, and in corners to reduce hiding places.
② Organize clutter: Avoid excessive accumulation of items like clothing, books, and cardboard boxes, which can serve as hiding spots. Regularly organize wardrobes by sorting clothes into sealed bags or storage containers to prevent bed bug infestation.
③ Maintain dryness: Bed bugs thrive in damp environments. Ensure rooms are well-ventilated and dry, preventing water buildup in bathrooms and kitchens. Consider using a dehumidifier to maintain indoor humidity below 50%, disrupting bed bugs’ survival conditions.
3. Furniture Maintenance: Repair Promptly and Seal Entry Points
Cracks and damage in furniture serve as key entry points for bed bugs. Conduct regular inspections and maintenance.
① Inspect bedding: Regularly check mattresses, bed frames, nightstands, and other bedding for cracks, damage, or loose parts. Fill any cracks in bed frames with putty; replace or repair damaged mattress surfaces promptly.
② Seal wall gaps: Inspect walls, ceilings, and floors for cracks or holes. Seal any found using caulk, plaster, or similar materials to prevent bed bugs from entering the room.
③ Exercise caution when purchasing secondhand furniture: Secondhand furniture is a major carrier for bed bug infestations. When buying such items, thoroughly inspect for signs of bed bugs (such as droppings, molted skins, or adult bugs). If purchasing secondhand furniture, first treat it with high-temperature processing or insecticide spraying. Only use the furniture after confirming it is free of bed bugs.
During bed bug control efforts, many people fall into common traps due to a lack of professional knowledge. Not only does this fail to effectively eliminate bed bugs, but it can also lead to their spread or pose health risks. Below are several prevalent misconceptions in bed bug control that require special attention.
1. Misconception 1: Believing “Clean Environments Are Bed Bug-Free”
Many assume bed bugs thrive only in dirty, cluttered environments and won’t infest clean homes. In reality, bed bugs primarily rely on “food (human blood)” and “hiding places” for survival—neither directly linked to cleanliness. Even immaculate homes can become infested if bed bugs enter (e.g., via luggage or secondhand furniture) and find suitable hiding spots. Therefore, one should not become complacent just because the environment is clean; preventive measures are still essential.
2. Misconception 2: Overusing Pesticides and Spraying Indiscriminately
Some people, seeking quick extermination, purchase large quantities of pesticides and spray them indiscriminately throughout rooms, even directly onto mattresses and clothing. This practice not only risks chemical residue that threatens human and pet health (causing respiratory infections, skin allergies, etc.), but also may breed insecticide resistance, complicating future control efforts. The correct approach is to select appropriate insecticides based on infestation levels and use them strictly according to instructions, avoiding excessive spraying.
3. Misconception Three: Discarding Mattresses and Furniture Upon Discovering Bed Bugs
When bed bugs are found on large furniture like mattresses or sofas, many people opt to discard them, believing this will resolve the issue completely. However, during disposal, bed bugs may cling to furniture surfaces and spread to hallways, elevators, or other residents’ homes during transport, causing broader contamination. Additionally, discarding furniture increases financial costs. The correct approach is to first treat the furniture with physical or chemical methods (such as high-temperature steam or insecticide spraying). If the issue persists after treatment, seal the furniture tightly (wrap it securely in plastic sheeting), label it with “Contains Bed Bugs,” and then dispose of it according to local waste disposal regulations.
4. Misconception 4: Believing “One Treatment Can Completely Eradicate the Problem”
Bed bugs reproduce rapidly and hide in numerous locations, making it difficult for a single treatment to eliminate all infestations—especially eggs and bugs concealed in deep crevices. Some people, seeking to save costs, assume the problem is solved after one treatment when no obvious activity is seen, neglecting subsequent monitoring and control. However, surviving bed bugs may reproduce again after some time, causing the infestation to recur. The correct approach is to conduct regular room inspections (e.g., checking bedding, crevices, etc.) for 1-2 months after the initial treatment. Only if no bed bugs are found can the problem be considered completely resolved. If bed bug activity is detected, treatment should be repeated promptly.
Though tiny in size, bed bugs pose significant hazards. Once infesting a home, they severely disrupt daily life and health. Therefore, it is essential to learn how to correctly identify bed bugs, understand their dangers, master scientific control and prevention methods, and avoid common treatment pitfalls. In daily life, prevent infestations by inspecting belongings after travel, maintaining clean living environments, and properly caring for furniture. If bed bugs are detected, promptly implement physical, chemical, or professional control measures based on the severity of the infestation to completely eradicate them. Only through such comprehensive efforts can we effectively safeguard our living spaces and protect our families’ health, truly bidding farewell to bed bug troubles.

Hola, soy el webmaster de lecintech.com, Robert Luo, puedes llamarme Robert. Tengo años de experiencia en el negocio de control de plagas. Nos especializamos en el diseño y fabricación de ahuyentadores ultrasónicos de plagas, ahuyentadores ultrasónicos de mosquitos, ahuyentadores ultrasónicos de roedores, ahuyentadores de animales alimentados por energía solar, trampas de plagas, ahuyentadores de plagas portátiles y mucho más.